The best Iranian shrimp producer and exporter
Last updates
Contact us
-
Office: Tehran, Iran
Facilities: BandarAbbass, Iran - Call: +98 912 3757303
- Whatsapp Message
- info@shrimpyco.com
Vannamei shrimp Specification
- Home
- Vannamei shrimp Specification

About
Vannamei shrimp
Nowadays, the Vannamei shrimp is farmed as a breeding species in numerous parts of the world. Also, it is the most popular type in Iran’s shrimp market. Considering the capacity to cultivate this shrimp in non-dense, semi-dense, thick and ultra-dense ways, this shrimp has the capacity to live in both brackish and brackish water. For this reason, a wide extend of topographical regions have the capacity to develop this species. Nowadays, most producers of this shrimp are in central and south American nations.
The normal living space of this shrimp is the eastern parts of the Atlantic Sea, the coast of Mexico, and the coastline of southern and central nations up to the coast of Peru. Normally, Vannamei chooses regions for living that have a temperature over 20 degrees all through the year. In common, the farming of this shrimp is within the waters around tropical zones.
Types of products
Shrimpy provide different types of products regarding to the customers needs and requests. You can choose from the bellow list.
Head-On Shell-On
- Size 30/40, 40/50, 50/60, 60/70, 70/80, 80/100,100/120
- A1 and A2 product quality, antibiotic and additive free
- Packages in 2 ways: 2 kg box in 12 kg master cartons and 6 kg block
Headless Shell-On
- Size 30/40, 40/50, 50/60, 60/70, 70/80, 80/100,100/120
- A1 and A2 product quality, antibiotic and additive free
- Packages in 2 ways: 2 kg box in 12 kg master cartons and 6 kg block
Peeled Tail-On
- Size 30/40, 40/50, 50/60, 60/70, 70/80, 80/100,100/120
- A1 and A2 product quality, antibiotic and additive free
- Packages in 2 ways: 2 kg box in 12 kg master cartons and 6 kg block
Peeled Un-Deveined
- Size 30/40, 40/50, 50/60, 60/70, 70/80, 80/100,100/120
- A1 and A2 product quality, antibiotic and additive free
- Packages in 2 ways: 2 kg box in 12 kg master cartons and 6 kg block
Peeled Deveined
- Size 30/40, 40/50, 50/60, 60/70, 70/80
- A1 and A2 product quality, antibiotic and additive free
- Packages in 2 ways: 2 kg box in 12 kg master cartons and 6 kg block
Why shrimp
Shrimp, like other seafood, is wealthy in calcium, iodine, and protein, which play an critical part within the food chain. Shrimp is the most choice of individuals who cherish fish since it is scrumptious and nutritious. Shrimp blended with uncommon herbs and flavors incorporates a incredible taste. Include the numerous wellbeing benefits of shrimp to its unique flavor and we have a super nourishment! Shrimp has numerous wellbeing benefits. It may be a normal remedy for people with tall blood weight (hypertension) and is wealthy in selenium, which has antioxidant properties. Shrimp makes a difference battle Alzheimer’s, frailty and could be a great source of protein and cholesterol. Agreeing to nutritionists, eating shrimp a week avoids Alzheimer’s and dementia in ancient age, since shrimp is wealthy in omega 3.
The healthiest food
Shrimp can be a special source of the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory carotenoid supplement astaxanthin. It is conceivable for a single 4-ounce serving of shrimp to contain 1-4 milligrams of astaxanthin.
Nutritional value per 100 g
Energy value
99 KCal
Proteins
24 gr
Сarbohydrates
0 gr
Fat
2 gr
Sodium
0.5 gr
Cholesterol
0.2 gr
Introduction of vannammei
Today, Vannamei shrimp is cultivated as a cultured species in many parts of the world, especially in Iran’s shrimp market. It is possible to farm this shrimp in non-dense, semi-dense, dense and ultra-dense methods, and this shrimp has the ability to live in both fresh and salt water. For this reason, this species can be grown in a wide range of geographical areas, and it is adaptable to Iran’s shrimp ecosystem.
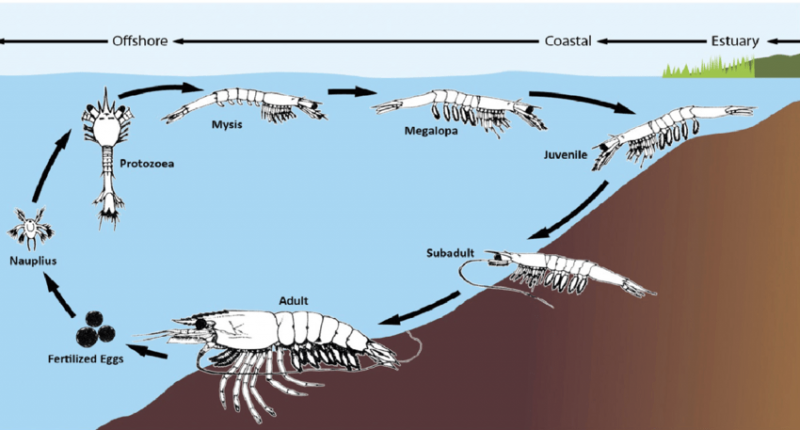
Adult shrimp release in living waters. in which the vannamei moves to the shallow shores during the larval stages until full maturity. Adult male Vannamei weighs 20 grams and adult female Vannamei weighs 28 grams and continues to gain weight throughout its life. Vannamei is ready to reproduce at a weight of 30 to 45 grams, and a female vannamei releases an average of 100,000 to 250,000 eggs in each spawning period.
The eggs break 16 hours after fertilization and the baby shrimp hatch. The shrimp larvae, called nauplius, swim continuously and are oriented toward the light. They do not feed on external food and feed on the remaining egg yolk. In the vannamei growth stages (protozoa, mysis, and the first post-larval stages), they lead a planktonic life and feed on phytoplanktons and zooplanktons and are guided to the shore by waves. Entering the post-larval stage about 5 days after molting causes a change in Vannamei’s diet, and after that, they feed on mollusks, crustaceans, and worms.

Vannamei shrimp life cycle
The maturation of vannamei in farming conditions takes about 4-5 months. After that, the fertilization process takes place and the fertile vannamei lay eggs. vannamei fertilization is a type of external fertilization. After two days of hatching, the result of this fertilization turns into a creature called Nauplius. They should be kept in special pools. Within 4-5 days, Nauplius reaches the next stage of its life called Protozoea.
4-5-day-old vannamei turns into zoa, at the age of 3-4 days into mysis, after 10-15 days into the post-larval stage, and finally after 3-5 months in dense pools, it reaches the juvenile stage. Juvenile shrimp raised in dense ponds reach a weight of about 15-25 grams and are ready to be collected and stocked in rearing ponds.
Dense shrimp farming system
In the intensive farming method of vannamei, closed ponds are used so that there are no currents like sea waves in them and the ability to completely drain them. It should be noted that the water outlet should be smaller than the size of the shrimps so that the shrimps do not get stuck in them. Another important point in this issue is that shrimps periodically molt and the size of these shells is larger than their body. As a result, having a water outlet smaller than the size of the shrimp’s body, it is possible to collect the shells dropped by the shrimps, which are mainly made of materials such as chitin and are considered added value.
Pools must be completely emptied and dried before each period of use in order to prepare them for use in the next period. In many Asian countries, swimming pools are installed away from sea water and run with low salinity water. This system is more popular in Asia and Latin America and gives better results depending on their climatic conditions. Many of these areas do not have natural access to salt water or brackish water. Shrimp ponds can be round or square and are usually small (0.1 to 1 hectare) and their water depth is more than 1.5 meters.
In each of these pools, between 60 and 300 post-larval shrimps are released per square meter. In pools above 400 to 600 kilos, the aeration and water circulation system is very important. Feeding with artificial food should happen at least 4 to 5 times a day. The food to weight conversion factor at this stage is about 1 to 1.4 to 1 to 1.8. vannamei does not get sick easily, but when buying shrimp, you can get your shrimp from reliable sellers who sell you disease-free or resistant domesticated shrimp.
Try to constantly check the water in your pools for biological contamination and in case of viral diseases, change your water to the minimum required amount. In the mentioned systems, it is possible to produce 7 to 20 tons of shrimps by careful feeding, providing high quality water and replacing it according to its size, feeding with phytoplankton and carefully checking the condition of shrimps. On average, by having three groups of shrimps with the mentioned conditions, 30 to 35 tons of shrimps can be produced.

Ultra-dense shrimp farming system
Recent ongoing research focuses on the intensive production of vannamei shrimp based on a greenhouse system. In these systems, there is no water exchange and the only water output of these systems is the result of evaporation. They keep these shrimps in water with very high oxygen and constant flow and use only shrimps immune to viral diseases.
These systems do not cause problems for the environment, have a relatively low running cost and produce high quality shrimp optimally. In these pools, 300 to 400 baby shrimp are released per square meter, and 28 to 68 tons of shrimp are produced in each period of 3 to 5 months. The food to weight conversion index in this method is 1 to 1.5 to 1 to 2.6.
vannamei farming is profitable compared to other types of shrimp farming and it is a relatively affordable way to earn money from the space available to the producer. One of these reasons is their lower need for protein in the diet (18-35% and 36-42% on average for other types). Ultra-dense breeding can yield up to five times more than other methods, with much less space for the grower.
A very important point in super-dense breeding is the control of water variables. The suitable PH for super-dense cultivation of vannamei is 7.5 to 8.7. Ventilation should be active and always in progress. Oxygen content of 4.26 ± 1.43 is required as a minimum for ultra-dense cultivation of vannamei. A temperature of 22 to 33 degrees Celsius is also ideal for growing vannamei.
Providing these conditions, according to the experiment conducted in Mexico, resulted in a survival rate of 95.8%. Daphne magna can be a good food for shrimps for the first 2 weeks. After that, they can be fed with pellets containing 35% protein. Pellets can be placed in the food basket. The mentioned experiment started with 35% salt water and then by adding fresh water, the salinity of the pool water decreased to 2.2% within 4 days.
Despite the fact that there are disease-resistant species in vannamei shrimp, and by purchasing shrimp from reputable sellers, the possibility of contracting the disease in this species can be greatly reduced. Any shape of your shrimps will be very helpful:
- Be sure to completely empty and dry the pool between both breeding periods
- Check the water entering your pool for biological contamination
- Use ropes for bird traps and scarecrows
- Build a fence around your pool
- Disinfect the water

Comparison of advantages of indicus and vannamei species
| Indicus shrimp | Vannamei shrimp |
|---|---|
| The indigenousness of the shrimp species | The growth of this species is fast |
| Natural breeding shrimp is available in suitable seasons | Within 120-150 days, it reaches the size of 40-50 for sale |
| Reproduction and production technology has been achieved over several years | Healthy and disease-free breeding shrimps (SPF and SPR) are available |
| It is a resistant species for the climatic conditions of Iran | Tolerating different climatic conditions (high or low salinity and high and low temperature). |
| Production is done only in Iran | The possibility of increasing production in the farm |
Comparison of disadvantages of indicus and vannamei species
| Indicus shrimp | Vannamei shrimp |
|---|---|
| The growth of this species is slow | It is an imported species and sometimes its import faces problems |
| Its F.C.R is high | We compete with countries such as China, Thailand, Vietnam and Latin American countries in terms of sales, prices and production |
| After 120-150 days, it reaches the size of 50-60 | Because it comes from a foreign country, it may contain unknown viruses |
| Its genetic modification is not available | In bad climatic conditions, it may suffer from loose shell and soft shell |
| Its production is not economical | The selling price is lower than Indicus |
Shrimp farming in Iran, Hormozgan
During this year, nearly 26.5 million vannamei shrimp fry were stored in 169 hectares of shrimp farms in the province, which were obtained from three sources, including larvae produced in Iran’s shrimp market, and shrimp fry produced from hatcheries imported from Hawaii.
In this area and due to the high salinity and environmental conditions, after the experiment of breeding green tiger and banana species, which were removed from the shrimp breeding cycle due to their own reasons. After the experts of Kolahi Aquaculture Development Center accidentally came across fast-growing shrimps in their breeding ponds in the early years of shrimp farming in Iran, it led to a change in the Iranian cultivated species and the Indian white species widely and commercially. should be cultivated in the country and the indicus species should be selected for cultivation.

Comparison of effective factors in production between indicus and vannamei
| Description | Indicus | vannamei |
|---|---|---|
| Breeding period | 130 to 150 days | 120 to 130 days |
| size | Maximum size between 15-18 grams | It easily reaches the weight of 20 to 25 grams |
| Density | 20 to 25 pieces per square meter without ventilation | 18 to 20 pieces per square meter without ventilation |
| Production per hectare | Maximum production of 2000 to 3000 kilos per hectare without aeration | Maximum production of 2500 to 4000 kilos per hectare without aeration |
| Maximum production per hectare with aeration | 3000 to 7000 kilos per hectare | 5000 to 10000 kilos per hectare |
| F.C.R | 1.3 to 1.8 | 1.2 to 1.5 |
| Food quality and required amount of protein | Between 42% and 38% of the required protein is animal protein | Between 35% and 38% of the required protein is vegetable protein and a small amount of animal protein |
© Shrimpy | All rights reserved by ABADIS Group


